Plants Are Important To The Development Of Karst Primarily Because - Plants are important to the development of karst primarily because THEY PRODUCE ACIDS. They are hybrid plants that contain new alleles.
Karst An Overview Sciencedirect Topics
Karst water 46 million cubic meters per year and building stone are the major public revenues with the result that the land surface collapses and the scenic environment is damaged.
Plants are important to the development of karst primarily because. Arid climates whether hot or cold support little karst. In general a typical karst landscape forms when much of the water falling on the surface interacts with and enters the subsurface through cracks fractures and holes that have been dissolved into the bedrock. Karst landscapes feature caves underground streams and sinkholes on the surface.
The development of all karst landforms requires the presence of rock which is capable of being dissolved by surface water or ground water. Factor because the basis of plant expression the gene is located within the cell. Support for birds and animals.
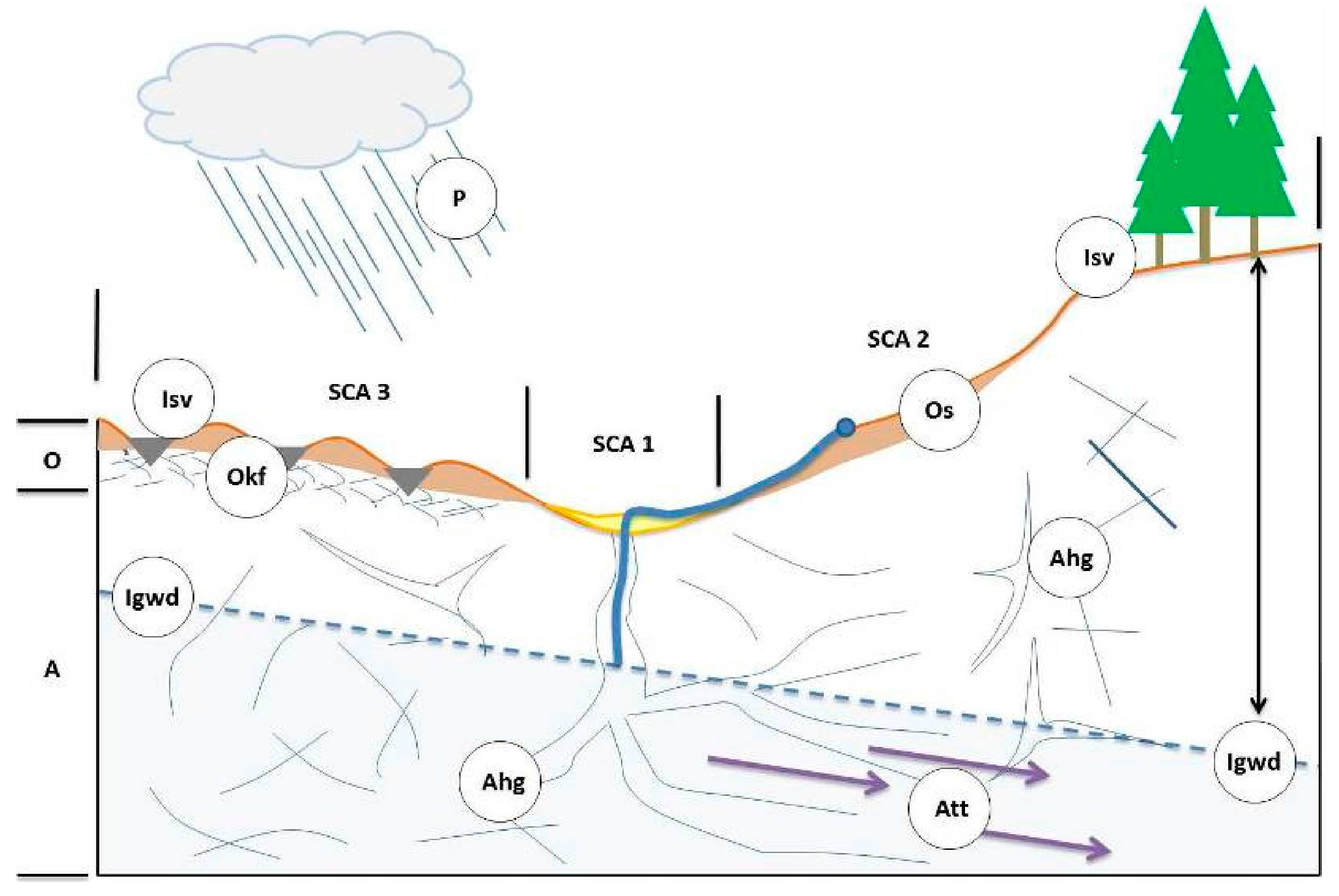
The term karst describes a distinctive topography that indicates dissolution also called chemical solution of underlying soluble rocks by surface water or ground water. Conditions that promote karst development are well-jointed dense limestone near the surface. They grow bacteria on the surface of leaves or roots that produce these moleculesC.
Plants are the best places of shelter for birds and few animals like monkeys squirrels to live. In Chinese shilin means stone forest. Karst is a special type of landscape that is formed by the dissolution of soluble rocks including limestone and dolomite.
The karst mountains are famous because of the. Leaves of this plant are rich in amino acids tea saponin polysaccharides flavonoids and other biologically active ingredients and has important medicinal functions includ-ing improving immunity lowering blood lipid and sugar levels and fighting cancer Wei Huang Jiang 2011. The development of karst is primarily dependent on the presence of soluble rocks.
Karst is a type of landscape a basin or small hill formed through erosion and dissolution of limestone CaCO 3 and dolomite CaMgCO 3 2 Hartmann et al 2014Twelve percent of Earths surface is covered by karst which stores water for 25 percent of the worlds population Radulović 2013Karst areas are unique and beautiful with soils that are characterised by high. Because the soil is shallow in the karst mountains soil samples were only collected at a depth of 015 cm at eight to ten random locations along an S-shaped transect in each plot. Shilin got its name because the tall rocks that formed due to erosion look like stone trees.
Therefore efforts to map karst distribution have normally taken a geology-based approach effectively delineating areas having potential for karst development by compiling areas of soluble rocks from geologic maps for example see Williams and Ford 2006. In forests animals can take shelter under trees in heavy summers and rain. Physical rock properties also are important.
Hopkins and Hüner 2004. Co-chairing the IUCN-SSC Specialist Group for Cave Invertebrates which aims to encourage a more environmentally sensitive approach to limestone quarrying. Karst features may also develop though rarely on very weakly soluble rocks such as basalt granite or quartzite.
Karst regions contain aquifers that are capable of providing large supplies of water. Karst areas associated with eastward flowing streams tend to have much vertical development and include many of the major cave areas of eastern Australia including Jenolan Colong Tuglow Wombeyan Bendethera and Wyanbene. More than 25 percent of the worlds population either lives on or obtains its water from karst aquifers.
Unfortunately because of the recent habitat loss and over-. Karst is associated with soluble rock types such as limestone marble and gypsum. The landscape is characterized by caves sink holes fissures and underground streams.
Among these projects ecological restoration projects are the most fundamental and essential measure for controlling karst rocky. Birds build their nests for hatching eggs sleep hunt and safety on the trees. Arid conditions Plants are important to the development of karst topography because.
Rock solubility and water are the primary factors in karst development. Humidity levels are especially important in allowing the plant to carry. The majority of these occur in the central and southern highlands of NSW and the adjacent incised stream headwaters.
By a karst landscape and covered by carbonate rocks that reach a depth of 4600 m see. The relationship of this abiotic factor to. Where erosion has worn away the land above ground steep rocky cliffs are visible.
A moderate to heavy rainfall. And why is it important. They have been injected with these new molecules and there is no natural method for them to be degraded in the organismD.
Identifying priority sites for karst biodiversity conservation in Myanmar and developing best practice guidelines for tourist cave management and limestone quarrying. Influences plant growth and development primarily through temperature effect. Shilin is a karst formation in southern China.
Openings adjacent to their roots serve as microchannels that allow water to enter the rock. And good groundwater circulation. Ecological restoration projects basic farmland construction projects karst water development and utilization projects rural energy engineering and ecological resettlement projects Liao et al.
Which of the following is not necessary for well-developed karst to develop. Limestone calcium carbonate dissolves relatively easily in slightly acidic water which occurs widely in nature. Five types of projects are being conducted.
Normally occurring molecules have been modified to serve different functionsE.
Influence Of Shale Gas Development On Core Forests In The Subtropical Karst Region In Southwestern China Sciencedirect
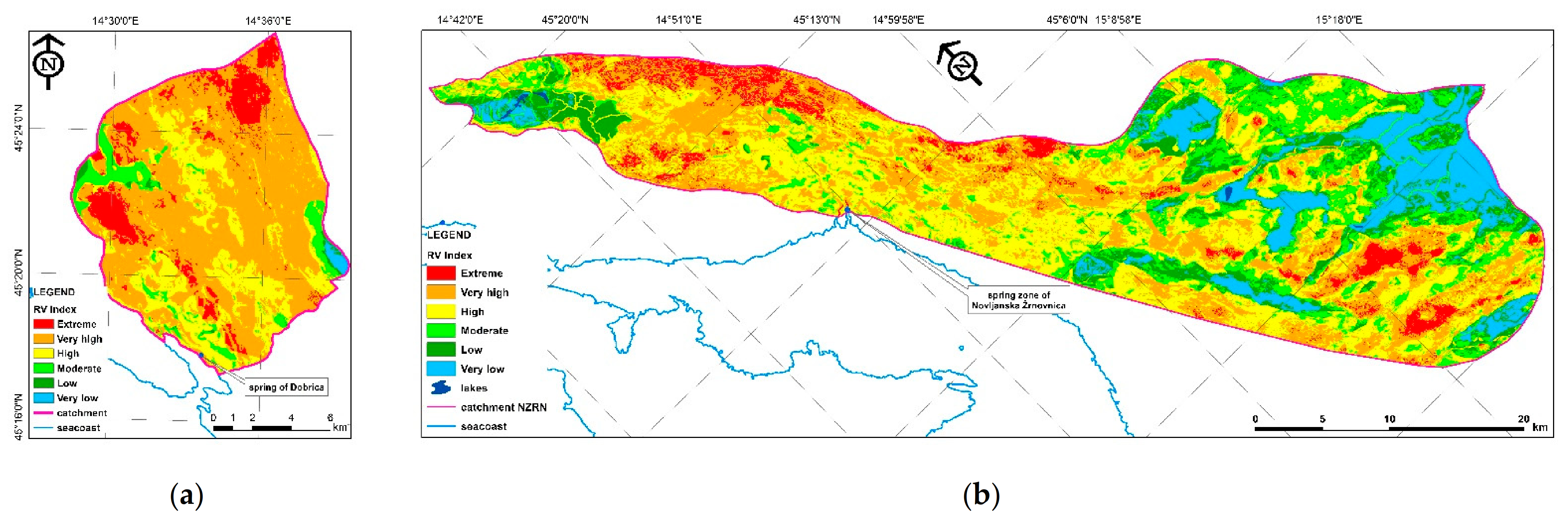
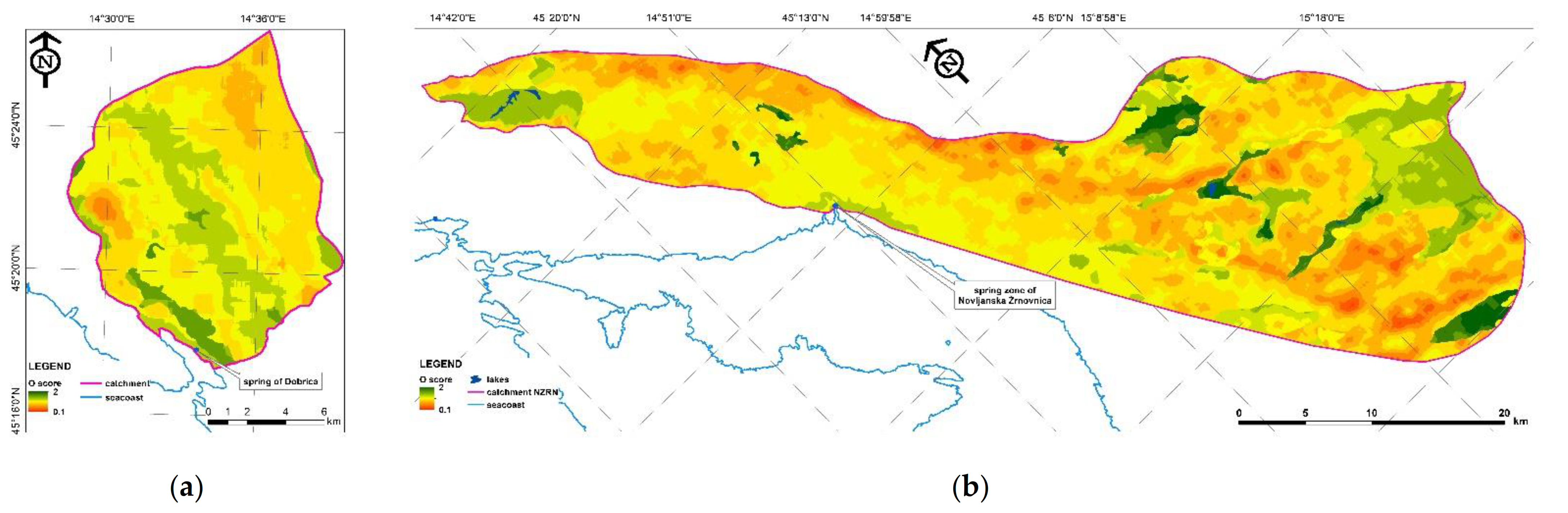
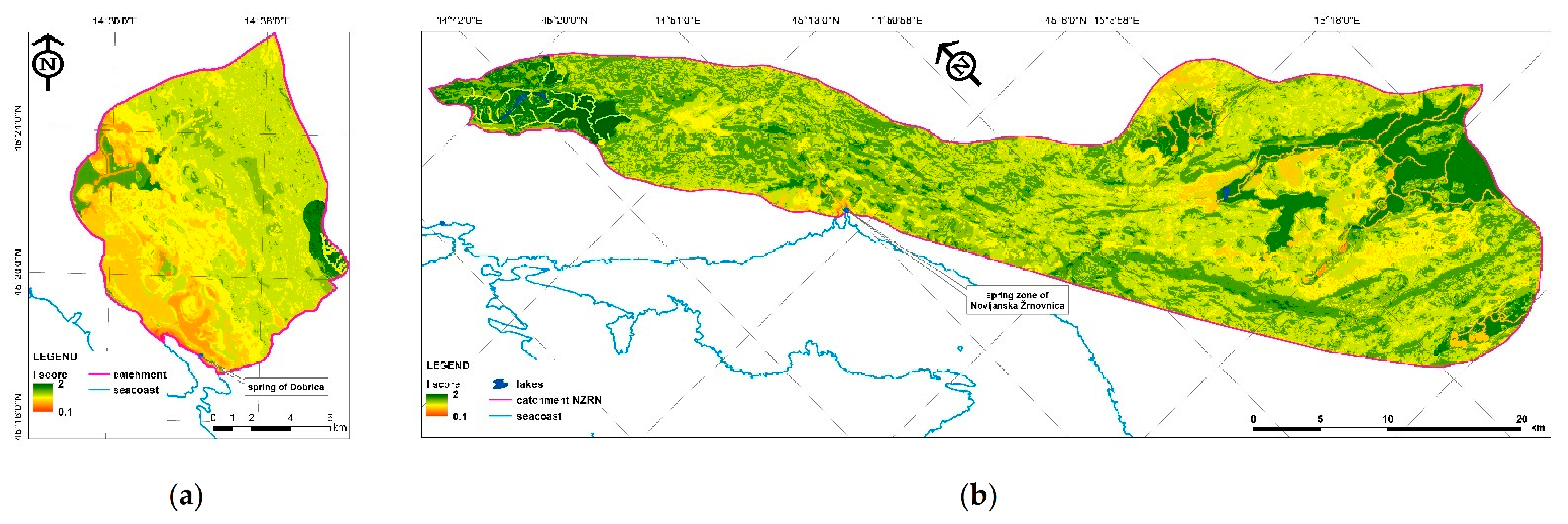
Sustainability Free Full Text Karst Aquifer Vulnerability Assessment Kava Method A Novel Gis Based Method For Deep Karst Aquifers Html
Sinkholes And Karst Terrain Regions In America 1900 2015 Maps Geological Data Map Of Florida Geology Florida
Pdf Karst And Paleokarst
Sustainability Free Full Text Karst Aquifer Vulnerability Assessment Kava Method A Novel Gis Based Method For Deep Karst Aquifers Html
Variation In Karst Morphology Broadly Described In An Engineering Download Scientific Diagram
Challenges In Transboundary Karst Water Resources Management Prof Dr Sc Ognjen Bonacci Faculty Of Civil Engineering And Architecture Split University Ppt Download
Karstification An Overview Sciencedirect Topics
Minerals Free Full Text Eogenetic Karst Control Of Carbonate Reservoirs During A Transient Exposure A Case Study Of The Ordovician Yingshan Formation In The Northern Slope Of The Tazhong Uplift Tarim
Karst An Overview Sciencedirect Topics
Distribution And Development Conditions Of Karst Phenomena In Estonia
Sustainability Free Full Text Karst Aquifer Vulnerability Assessment Kava Method A Novel Gis Based Method For Deep Karst Aquifers Html
Sustainability Free Full Text Karst Aquifer Vulnerability Assessment Kava Method A Novel Gis Based Method For Deep Karst Aquifers Html
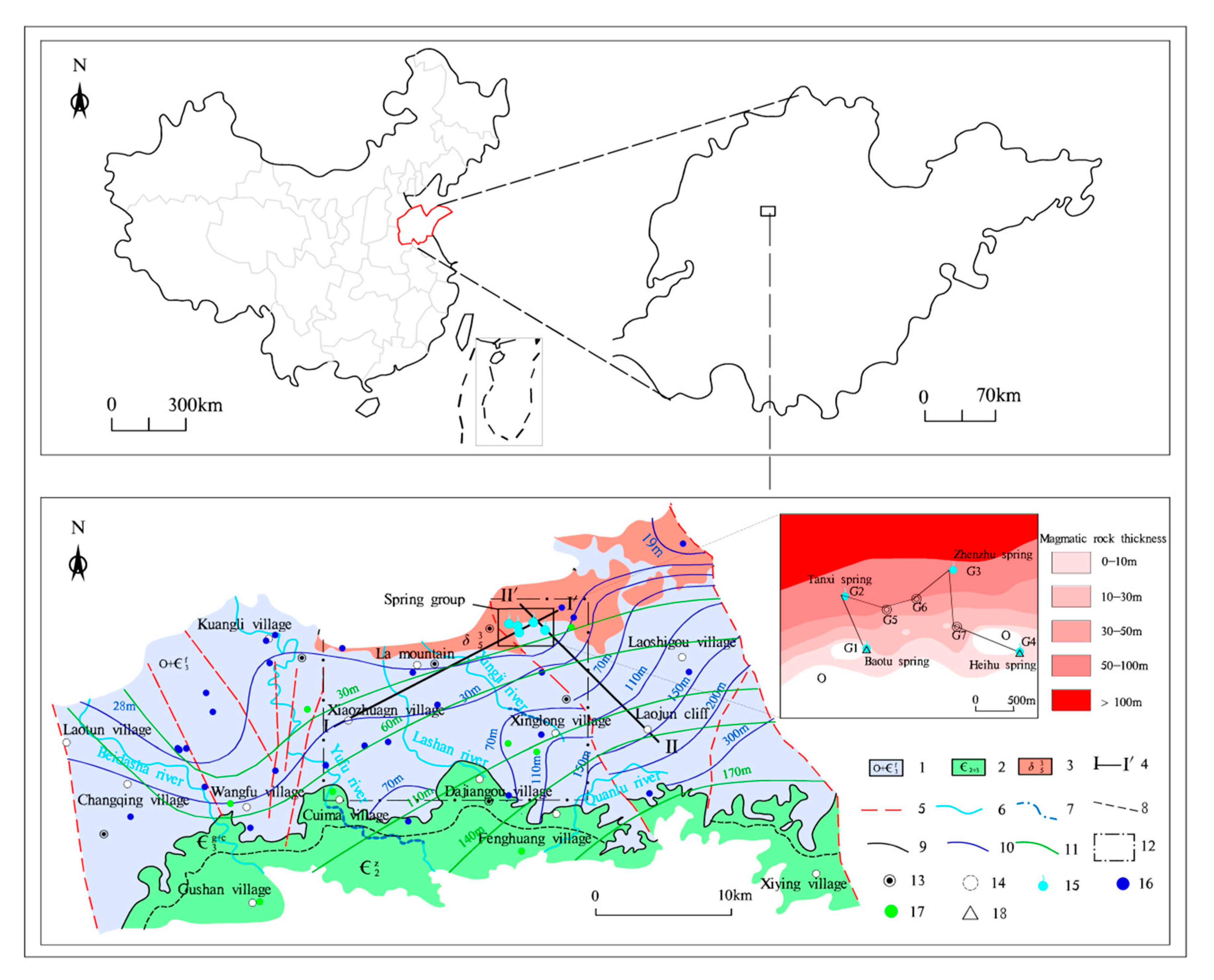
Water Free Full Text Water Recharge Of Jinan Karst Springs Shandong China Html